The casting industry is a manufacturing sector that creates products by pouring materials in a liquid state into molds to produce items with shapes identical to the mold. This process is carried out with materials such as metals or plastics. The growth of this industry creates opportunities for the development of both heavy and light industries.
Automation in the casting industry involves applying technical solutions to replace human labor in various production stages. The application of automation in this field is suitable for industries that require high precision and excellent surface finishes, such as the automotive and motorcycle industries.
Machines Used
- Automated Casting Systems: These systems include robotic arms that handle mold preparation, pouring molten metal, and transferring molds through different stages of the process.
- Metal Injection Machines: These machines ensure that molten metal is poured with precision and controlled pressure, reducing the chances of air pockets and defects.
- Cooling Stations: The cooling systems control the temperature and speed of the cooling process to ensure uniformity in the final cast product, avoiding cracks or deformations.
- Mold Preparation Systems: Automated systems that prepare and condition the molds for casting, ensuring proper alignment and surface smoothness.
Applications in Industry
Our casting solution is highly versatile and can be applied across various industries that require the production of durable and complex metal parts:
- Automotive: Casting of engine blocks, transmission housings, and other components that require strength and precision.
- Industrial Machinery: Production of large and small parts used in heavy machinery, construction equipment, and industrial tools.
- Consumer Products: Casting of metal parts for household appliances, hardware, and other consumer goods requiring high durability.
- Aerospace: Precision casting for components in the aerospace industry that require lightweight and strong metal parts.
Customer Use Cases
- Pioneer: Uses our casting solution to produce intricate metal parts for audio systems, ensuring durability and high performance.
- Nissei Technology: Applies automated casting for the production of precision parts used in industrial machinery and high-tech equipment.
- Vinfast: We use our casting solution for automotive components, such as engine housings and structural parts, to provide high strength and precision for their vehicles.
Benefits
- High Precision and Quality: The automated casting systems ensure precise pouring and cooling, resulting in cast parts with high dimensional accuracy and minimal defects.
- Increased Productivity: By automating the entire casting process, manufacturers can significantly reduce production times, allowing for higher output without sacrificing quality.
- Cost Savings: Automated processes reduce material waste and minimize labor costs, providing a cost-effective solution for high-volume casting needs.
- Consistency and Reliability: Automation ensures that every casting cycle produces parts of the same high quality, ensuring consistency across production runs.
- Adaptability: The system can easily adapt to different casting materials and product designs, providing flexibility for manufacturers across various industries.
ETEK’s Robotic Automation Solution for Plastic Injection Molding Machines
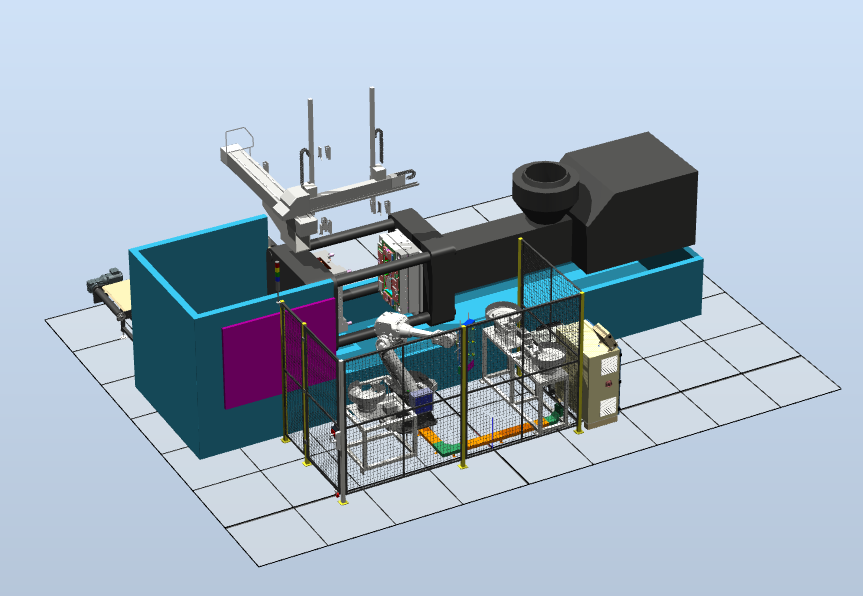
ETEK experts surveyed production operations, analyzed challenges, and designed a tailored robotic automation solution for plastic injection molding plants. This solution has significantly improved efficiency.
Robot Tasks in the Plastic Injection Molding Plant
- Insert components into the plastic mold.
- Retrieve finished products from the mold.
System Operation Principles
- Step 1: Insert components are sequentially fed from the feeder and positioned on the robot. Once all parts are inserted into the tool, the robot moves to a standby position.
- Step 2: After molding is completed, the injection machine opens the mold, and the pre-programmed robot system quickly and accurately retrieves the product.
- Step 3: The robot moves to the mold’s insert position and inserts the required components into the mold in a coordinated manner.
- Step 4: At the end of the cycle, a monitoring camera inspects the final product and detects any defects (if present), preventing potential errors that could impact the entire production line.