Agriculture is a sector that includes both crop cultivation (such as wheat, grains, etc.) and animal husbandry. In this industry, automation plays an increasingly important role. The nature of agriculture requires a large workforce and production on a significant scale. Therefore, automation has become essential to optimize processes and harness the full benefits this technology brings. By integrating automation, farms can increase efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve productivity, leading to higher outputs and more sustainable practices. Furthermore, as the demand for food rises globally, automation helps meet these challenges more effectively. Consequently, the development of automated solutions in agriculture is critical for the future of food production.
Similar to other industries, automation in agriculture involves the use of modern machinery and equipment to replace human labor, aiming to enhance labor productivity and free people from heavy workloads.
By applying machinery, robots, and intelligent control systems to automate many processes in agricultural production, many companies have introduced specialized robots for the industry today.

Some processes that companies have automated include:
The advantages of automation in agriculture include:
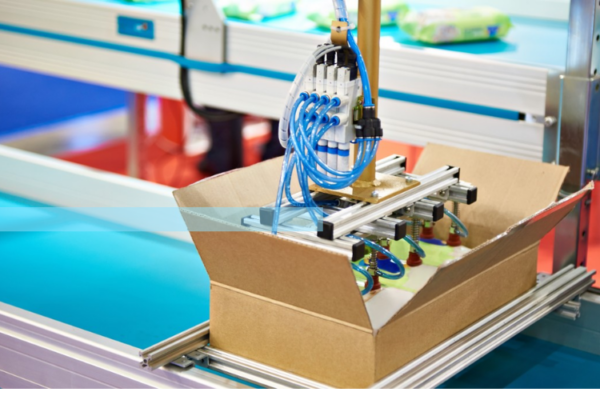

The case packer machine is a modern solution designed to optimized the automatic packaging process for bagged products. With its quick, precise and flexible operation, the machine not only increases…
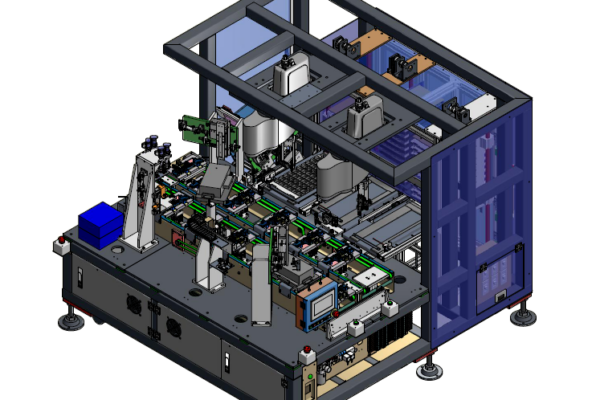
What is Automation Inserting? In our daily lives, we frequently encounter products assembled from numerous components, such as TVs, phones, laptops, and computers. The assembly process of these products involves…
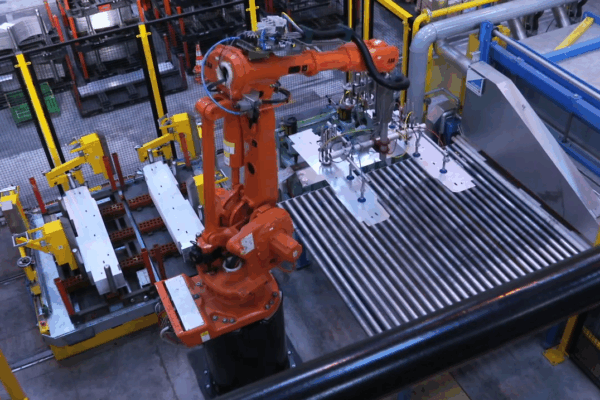
In the context of the booming Industry 4.0, metal stamping automation is no longer an option but a mandatory trend if businesses want to increase productivity, ensure quality and minimize labor risks. Industrial…
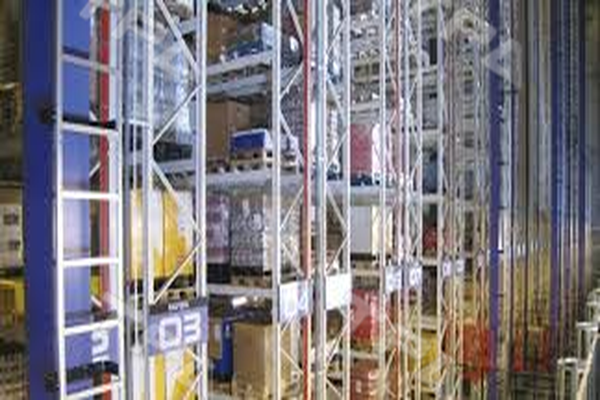

The high-density, high-speed, and flexible pallet storage system makes ETEK’s Automated Storage and Retrieval System (AS/RS) for pallets one of the most advanced automated warehousing solutions on the market. With…