In recent years, Vietnam’s automotive industry has witnessed remarkable progress, largely due to the adoption of modern technologies in automotive assembly systems. This advancement has not only improved product quality but also enabled the industry to produce vehicles competitive in international markets, solidifying its position in the global automotive landscape.
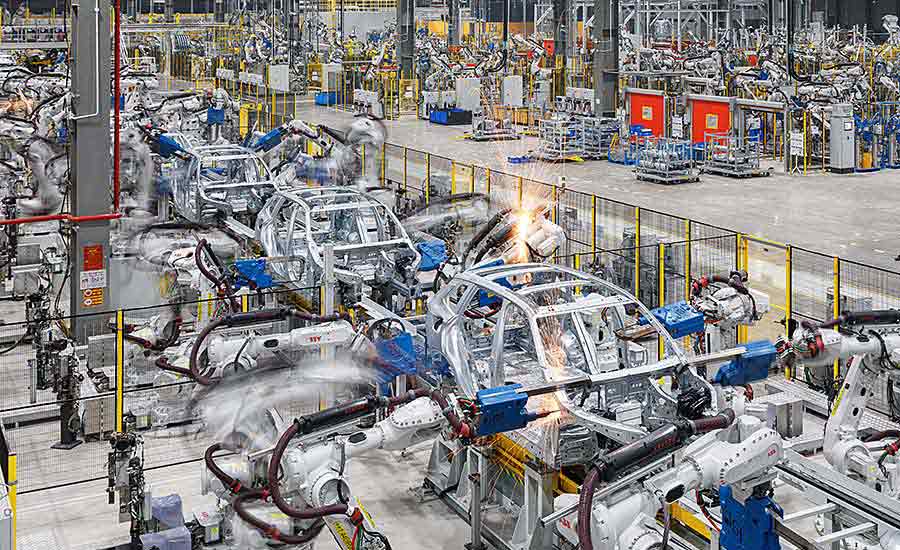

Many people attribute the invention of the automotive assembly line to Henry Ford. However, the concept was initially developed by Ransom Eli Olds, a pioneer in automobile manufacturing between 1901 and 1904.
In 1908, Henry Ford enhanced Olds’ design, achieving a significant breakthrough in production efficiency. With the ambition to create a flexible production line, he began by applying conveyors combined with pull and pulley systems. By 1913, Ford transitioned to a chassis assembly line, and in February 1914, his mechanical conveyor belt reached a speed of 6 feet per minute, marking a milestone in the automotive industry.
Since then, automotive assembly lines have been continuously improved, evolving from simple manual techniques to fully automated systems, playing a pivotal role in shaping the modern automotive industry.
An automotive assembly line is an integrated system of automated and semi-automated equipment designed to perform sequential and continuous production processes. This system leverages advanced technologies to assemble components into a complete vehicle efficiently and effectively.
Essential equipment for operating an automotive assembly line includes:
Additionally, the assembly line is equipped with guiding and supporting components such as:
The combination of these advanced devices ensures smooth operation, enhances efficiency, and guarantees quality during the vehicle production process.
Automotive assembly lines represent a significant advancement in the manufacturing industry, improving operational efficiency and ensuring superior product quality.
The automotive assembly process is optimized with advanced technologies, enhancing production efficiency and ensuring high-quality products. Key stages include:
The chassis serves as the primary load-bearing structure and protects passengers during use. The process begins with welding, cutting, and machining to ensure absolute accuracy. Once completed, the chassis moves to the assembly line, where components such as suspension systems, fuel tanks, drive shafts, transmissions, and brakes are systematically installed.
After the team prepares the chassis, they install body components such as doors, windows, and roofs. Robotic arms weld and connect details, replacing humans in tasks that require high precision and safety.
The vehicle’s surface is coated with paint to protect against corrosion and enhance aesthetics. Automated spray painting systems ensure an even and accurate finish, reducing human intervention and guaranteeing precise coloration.
During this stage, interior details such as seats, dashboards, electrical systems, and other components are installed. This phase combines automated technology with skilled technicians to ensure precision and completeness.
Once the body and chassis are ready, they are joined to form a complete structure. Robotic arms lift the vehicle body and attach it to the chassis, while technicians perform tasks like securing components with bolts and installing wheels and braking systems.
Every vehicle undergoes a comprehensive quality inspection before leaving the factory. Tests include engine performance checks, safety system evaluations, and functionality assessments to ensure compliance with technical and quality standards.
This process ensures that each vehicle is manufactured with high accuracy, combining advanced technology and stringent quality control.
Automotive assembly line technology not only plays a crucial role in optimizing production processes but also drives the robust development of Vietnam’s automotive industry.
With the modernization of assembly lines, domestic automakers can increase productivity, reduce costs, and improve product quality, creating vehicles that meet international standards and paving the way for strong export opportunities.
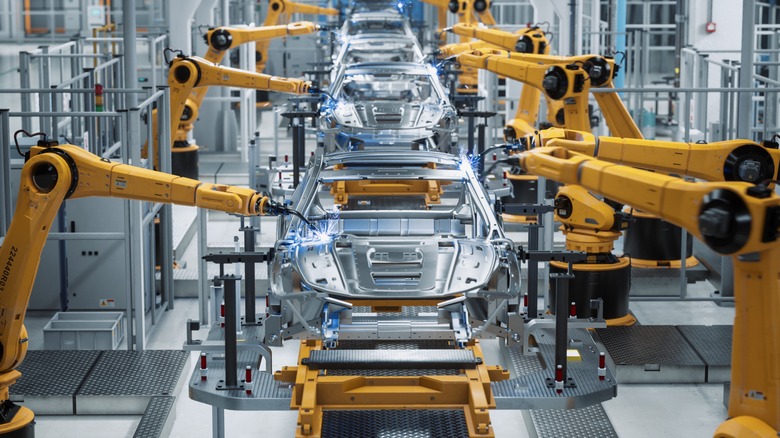

ETEK takes pride in being a pioneer supplier in developing and manufacturing technology products for Vietnam’s automobile production lines. We provide automated machinery systems, specialized equipment, and process optimization solutions. Our goal is to help you boost productivity, reduce costs, and enhance product quality.
>>> Learn more about ETEK’s assembly solutions here: https://etekautomation.com.vn/assembly-solution-overview
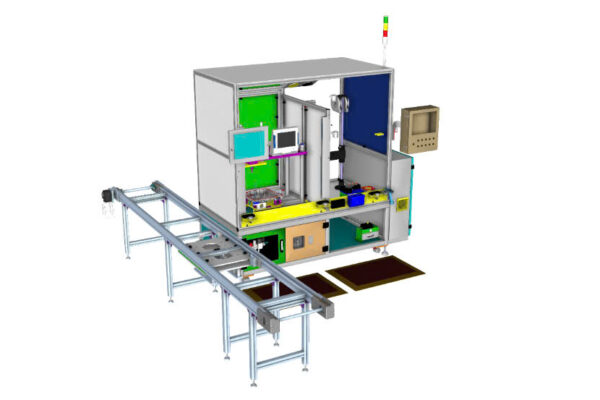
In industrial production lines, every assembly step plays a vital role in ensuring the quality of the final product. One of the key steps is pin pressing, which helps secure…
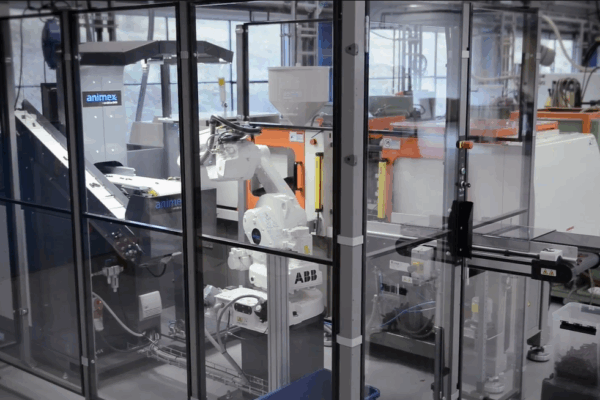
Are you looking for an efficient automation solution for your plastic molding station? ETEK provides comprehensive automated robot solutions, helping businesses improve productivity, reduce labor costs and ensure stable product…
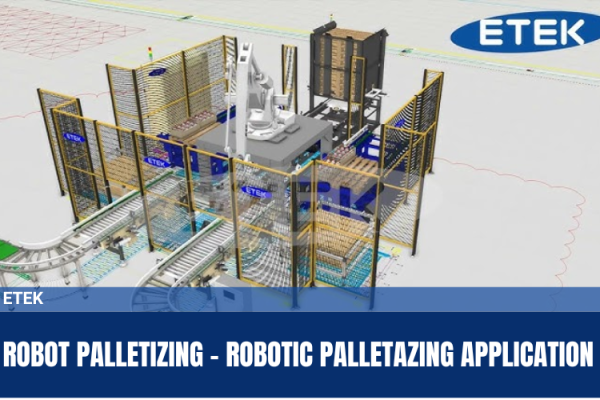
In industrial production, one of the stages prioritized for automation is the loading and unloading of go ods... From now on, businesses should turn automation solutions into their competitive advantage…

Introduction to the Automatic Packaging Line Automatic packaging lines have become an essential part of modern manufacturing plants, especially in industries such as food and beverage, consumer goods, pharmaceuticals, and…