In the past, before automation technologies were developed, screwing was primarily done manually using simple tools that relied on human labor, such as screwdrivers, handheld screw guns, and similar devices. Nowadays, thanks to advancements in science and technology, the screwing process has been gradually replaced by more optimal and efficient automated systems.
Screw automation refers to the process of using automated systems or robots to perform screwing tasks in production instead of relying on human labor. This technology has been widely applied in production lines to improve productivity, minimize errors, and save time.
A modern automated screw system typically includes the following components:
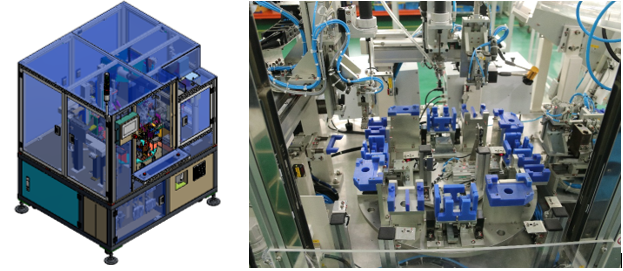
Automation is widely applied in industries across Vietnam and the world, offering numerous advantages, such as:
Thanks to its outstanding advantages, screw automation is now widely used across various industries, including:
In the ever-evolving landscape of science and technology, automation is increasingly being adopted. This inevitable trend of the era not only drives societal development but also liberates humans from labor-intensive tasks.
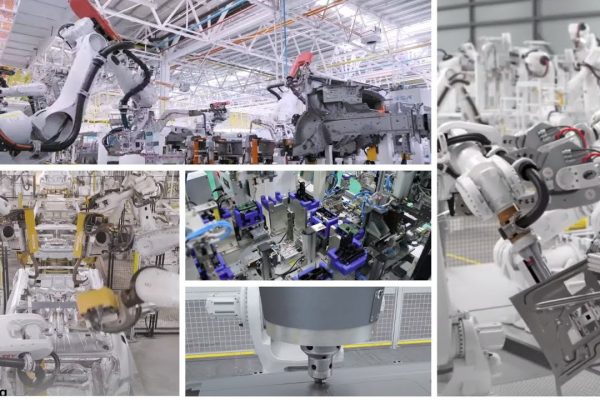
Our Assembly Solution is designed to enhance production efficiency, accuracy, and output while minimizing human intervention. By integrating advanced robotics, automated conveyance, and vision-guided technology, the system ensures precision in…

What is Gluing Automation? Since ancient times, people have known how to bond materials, seal, or protect surfaces by manually applying, spreading, or spraying adhesive using simple tools. This traditional…
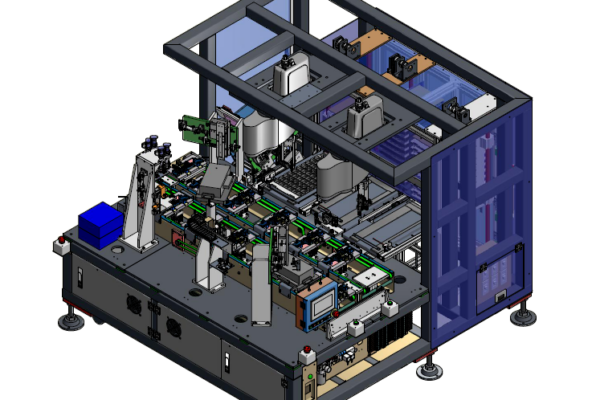
What is Automation Inserting? In our daily lives, we frequently encounter products assembled from numerous components, such as TVs, phones, laptops, and computers. The assembly process of these products involves…

What is Riveting Automation? To join parts together, in addition to methods such as screw fastening, welding, or adhesive bonding, people also use the riveting method in specific locations. Riveting…