Entering the industrial revolution 4.0, many businesses around the world are gradually focusing on investing in the development and production of service (support) robots. Industrial welding robots are one of the most widely used robots.
Industrial welding robots are a type of mechanized tool that completely automates the process by both performing welds and processing welded parts.
Specialized industrial welding robots
Each type of industrial welding robot used in automated lines is designed and manufactured with the highest precision. Their expertise lies in handling complex machining positions that require high accuracy, such as in the production of cars, motorcycles, etc.
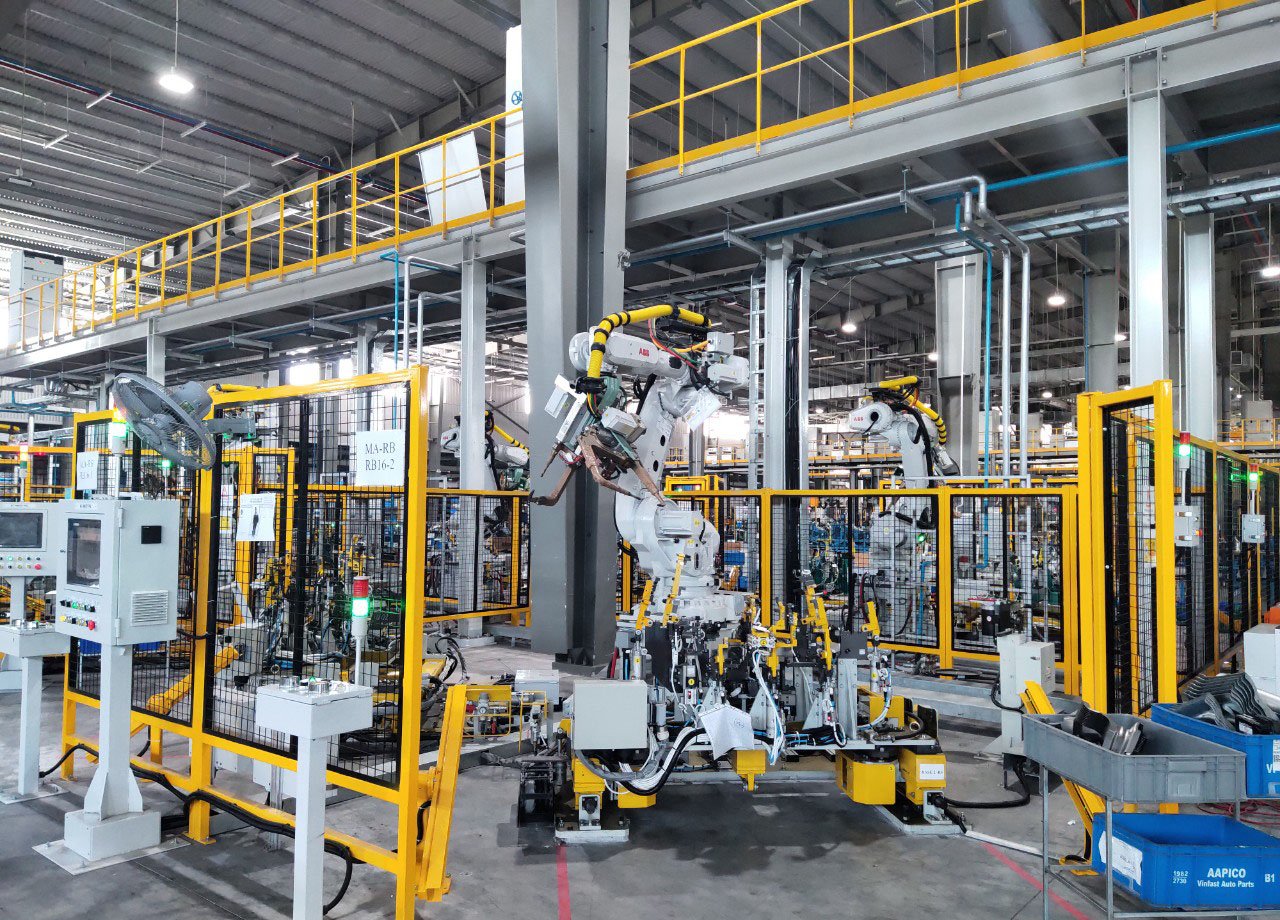

The welding workpiece needs to be held steady so that the welding robot can operate as required.
.jpg)
Options include collision sensors to avoid contact with soldering irons or other dangerous equipment.
Pressure sensitive safety mats and personal protective equipment.
HMIs can be simple or complex, depending on the application. Includes a button or an array of switches or a multi-screen computer application that controls all aspects of the work (e.g., part positioning, sensor monitoring, discharge parts, and transport to the next station).
It is important to consider the level of access for different people working with the device. For example, what features should be regulated by the operator and which should be restricted to programmers or maintenance technicians?
In some applications, the handheld device allows the operator to easily program the robot’s movements and store them as a program to run. Other applications, especially those that run at high speeds or with short cycle times, require more programming experience.
FOR MORE INFORMATION, PLEASE CONTACT ETEK AUTOMATION SOLUTIONS JOINT STOCK COMPANY
Water heaters are essential appliances in every modern household, requiring precise, safe, and consistent manufacturing processes. With extensive experience in production automation, ETEK provides automated water heater assembly line solutions…

Overview The plastic parts painting line supplied by ETEK has been successfully commissioned and is operating stably at the factory, meeting high requirements for surface quality and production stability. This…
Our Welding Solution offers an advanced, fully automated system for performing a wide range of welding tasks with precision and consistency. This solution is ideal for industries that require strong,…

In the era of modern industry constantly developing, automation technology has been reshaping the way manufacturing industries operate, helping businesses improve efficiency and reduce costs. In particular, in the automobile…